How UI-TARS actually works
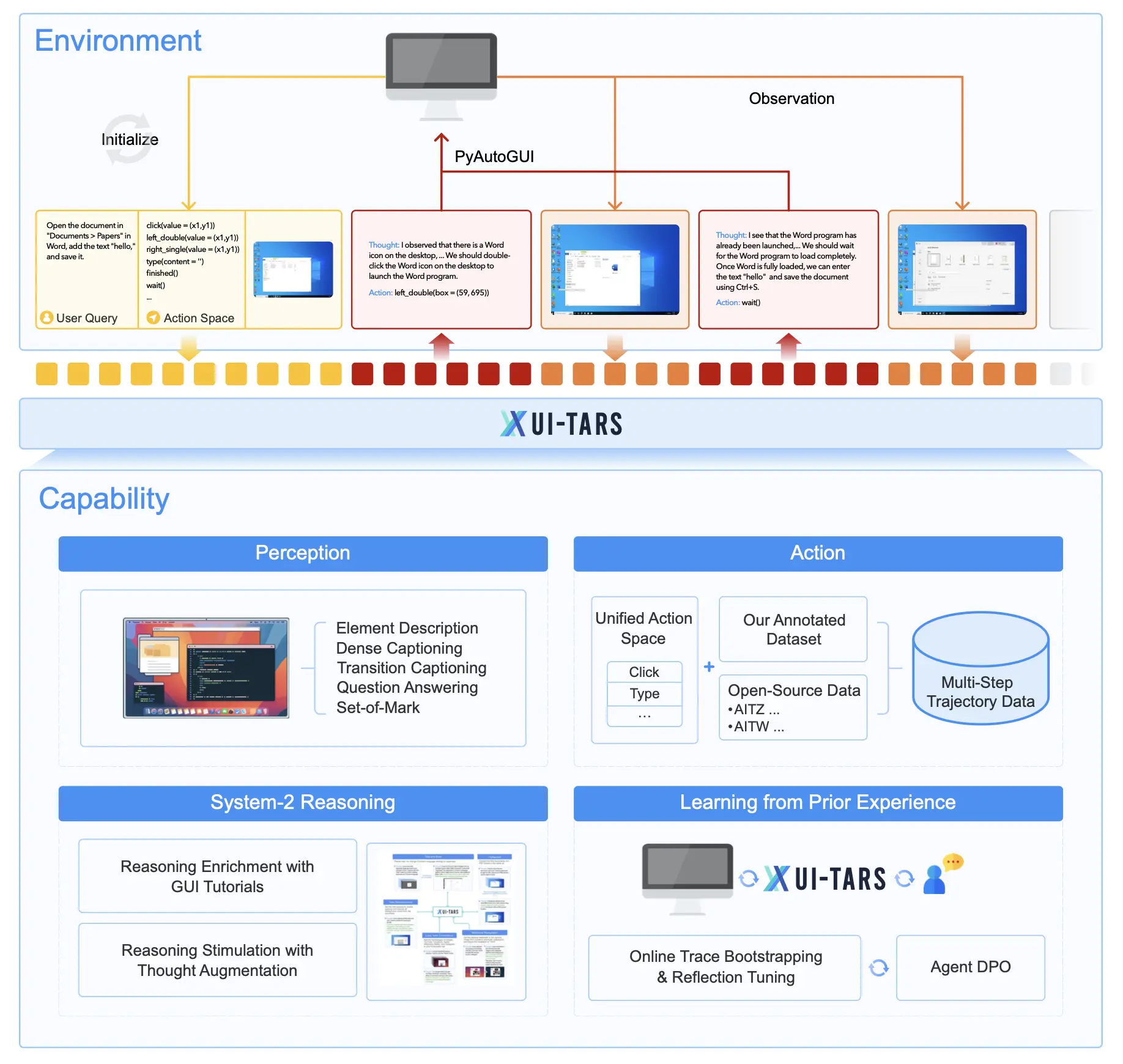
UI-TARS represents a fundamental departure from traditional GUI automation tools by integrating perception, reasoning, action, and memory into a single end-to-end model. Unlike frameworks that rely on wrapped commercial models with predefined workflows, UI-TARS uses a pure-vision approach that processes screenshots directly.
The architecture comprises four tightly integrated components:
Perception System: Processes screenshots to understand GUI elements, their relationships, and context. The model identifies buttons, text fields, and interactive components with sub-5-pixel accuracy, allowing for precise interactions.
Reasoning Module: Employs both System-1 (intuitive) and System-2 (deliberative) reasoning. For complex tasks, UI-TARS generates explicit “thoughts” that reflect its decision-making process—similar to how humans might pause to think through a challenging interface.
Action System: Provides a unified framework for standardizing actions across platforms, including mouse operations, keyboard inputs, mobile gestures, and system navigation commands.
Memory Component: Stores task-specific information and relevant background knowledge, enabling the model to maintain context across extended interactions.
The system works through an iterative execution loop: receiving a task instruction, processing visual input, generating reasoning thoughts, executing actions, observing results, and repeating until completion. This approach allows UI-TARS to adapt to unfamiliar interfaces without requiring predefined workflows.
Choose your model: capabilities across different sizes
ByteDance offers UI-TARS in three main parameter sizes, each with different capabilities and performance characteristics:
UI-TARS-2B (2 Billion Parameters)
This lightweight model excels in resource-constrained environments like edge devices and mobile platforms. With a ScreenSpot accuracy of 82.3% and OSWorld benchmark (15 steps) success rate of ~14-15%, it’s suitable for simple GUI tasks with clear interfaces. Its primary advantage is minimal computational requirements, making it accessible for deployment on standard consumer hardware.
UI-TARS-7B (7 Billion Parameters)
The mid-sized model strikes an optimal balance between performance and efficiency. It achieves a leading score of 93.6% on the WebSRC benchmark and 89.5% on ScreenSpot accuracy. With an OSWorld benchmark (15 steps) success rate of 18.7% and an AndroidWorld task completion rate of ~40%, it’s ideal for general computer use, browser automation, and daily productivity tasks.
UI-TARS-72B (72 Billion Parameters)
The full-sized model delivers maximum capabilities, outperforming GPT-4o with an 82.8% score on VisualWebBench (vs. GPT-4o’s 78.5%) and 88.6% on ScreenQA-short. It achieves 24.6% success on OSWorld (50 steps) and 22.7% on OSWorld (15 steps). This model excels in complex multi-step workflows, gaming environments, and enterprise automation, though it requires substantial computational resources.
The newest release, UI-TARS-1.5 (April 2025), comes in both 7B and 72B versions with significantly enhanced reasoning capabilities. The 7B version is optimized for general computer use, while the full version specializes in gaming and complex scenarios but has more limited availability.
Leaving competitors behind: performance benchmarks
UI-TARS consistently outperforms competing models across all major benchmarks, solidifying its position as the leading GUI automation agent.
In the OSWorld benchmark, UI-TARS-1.5 achieved a 42.5% success rate on 100-step tasks, compared to OpenAI Operator’s 36.4% and Claude 3.7’s 28%. This benchmark evaluates the ability to handle complex, open-ended computer tasks across various applications.
For GUI perception, UI-TARS-72B scored 82.8% on VisualWebBench, outperforming GPT-4o (78.5%) and Claude 3.5 (78.2%). On the WebSRC benchmark, UI-TARS-7B achieved an impressive 93.6%, surpassing all competitors.
Perhaps most striking is UI-TARS’s performance in ScreenSpotPro, which tests precise GUI grounding. UI-TARS-1.5 scored 61.6%, dwarfing OpenAI Operator’s 23.4% and Claude 3.7’s 27.7%. This translates to significantly more reliable interactions with interface elements.
UI-TARS also demonstrates superior cross-platform capabilities, particularly in mobile environments. On the AndroidWorld benchmark, UI-TARS reached 46.6%, compared to GPT-4o’s 34.5%, highlighting its versatility across different operating systems and device types.
From automation to augmentation: real-world applications
UI-TARS excels in diverse practical applications that showcase its versatility across platforms and task types.
Productivity Automation
UI-TARS can handle complex workflows that previously required manual intervention. In demonstration videos, it successfully completed tasks like:
- Installing the AutoDocstring extension in VS Code by navigating the application interface, accessing the Extensions view, and completing the installation process
- Opening files in specific applications, making edits, and saving them to specified locations
- Configuring application settings according to detailed requirements
Software Testing and Quality Assurance
The ability to navigate interfaces like a human user makes UI-TARS particularly valuable for software testing:
- Executing test cases across different platforms without requiring separate automation scripts
- Identifying visual inconsistencies and usability issues
- Performing validation tests with natural language specifications rather than coded scripts
Customer Service Automation
Companies are implementing UI-TARS to handle interface-dependent customer service tasks:
- Walking customers through complex setup procedures
- Troubleshooting application issues by directly interacting with the software
- Completing administrative tasks that require navigation across multiple systems
Gaming Environments
UI-TARS-1.5 demonstrates remarkable gaming capabilities, achieving a 100% task completion rate across 14 mini-games in the Poki Games benchmark. This performance extends to more complex gaming environments like Minecraft, where the model can execute specific building tasks and game objectives.
Accessibility Applications
The technology is being adapted to assist users with physical limitations, enabling natural language control of interfaces that might otherwise require precise mouse or touch interactions.
Getting started: setup and installation guide
UI-TARS Desktop Setup
Download the Application:
- Visit the UI-TARS Desktop releases page
- Download the appropriate version for your system (Windows: .exe, macOS: .dmg)
- Alternative: Use Homebrew on macOS (check GitHub for latest command)
Grant Required Permissions:
- Windows: Follow standard installation process
- macOS: Navigate to System Settings > Privacy & Security and grant permissions for Accessibility and Screen Recording
Configure Model Settings:
- Using Hugging Face for UI-TARS-1.5:
Language: en VLM Provider: Hugging Face for UI-TARS-1.5 VLM Base URL: https://xxx (your endpoint) VLM API KEY: hf_xxx (your API key) VLM Model Name: xxx (your model name)- Using VolcEngine Ark for Doubao-1.5-UI-TARS:
Language: cn VLM Provider: VolcEngine Ark for Doubao-1.5-UI-TARS VLM Base URL: https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3 VLM API KEY: ARK_API_KEY (your API key) VLM Model Name: doubao-1.5-ui-tars-250328Select Usage Scenario: Choose between Computer Operator or Browser Operator mode
Begin Using UI-TARS: Input your command to start automating tasks
Midscene.js Setup
For web and Android automation, Midscene.js offers multiple implementation options:
Chrome Extension (for quick experience without code):
- Install from Chrome Web Store
- Configure with appropriate model settings
JavaScript SDK (for developers):
- Install via npm:
npm install @midscene/web - For Android automation:
npm install @midscene/android
- Install via npm:
Configure for UI-TARS Model:
OPENAI_BASE_URL="..." # Your UI-TARS endpoint OPENAI_API_KEY="..." # Your API key MIDSCENE_MODEL_NAME="..." # Your UI-TARS model name MIDSCENE_USE_VLM_UI_TARS=1 # Enable UI-TARS mode
The competitive landscape: how UI-TARS compares to alternatives
UI-TARS offers several distinct advantages compared to similar GUI automation tools, while also facing certain limitations.
Advantages over competitors
End-to-End Architecture: Unlike frameworks that wrap existing models, UI-TARS integrates perception, reasoning, and action in a single model, resulting in more cohesive behavior.
Cross-Platform Capabilities: While tools like OpenAI’s Computer Use Assistant excel primarily in desktop environments, UI-TARS demonstrates superior performance across web, desktop, and mobile platforms.
Advanced Reasoning: UI-TARS implements both System-1 (fast/intuitive) and System-2 (deliberate) reasoning, enabling it to handle complex decisions more effectively than most competitors.
Open-Source Availability: Unlike closed commercial models, UI-TARS is freely available for both commercial and non-commercial use under the Apache 2.0 license.
Error Recovery: Through reinforcement learning and reflection-enhanced techniques, UI-TARS demonstrates better adaptation to unexpected situations and recovery from mistakes.
Disadvantages compared to alternatives
Computational Requirements: UI-TARS requires more substantial computational resources than some alternatives, particularly for the larger models.
Hallucination Issues: May occasionally generate inaccurate descriptions or misidentify UI elements, though at lower rates than most competitors.
Security Concerns: Enhanced GUI performance could potentially be exploited for unauthorized access or bypassing authentication challenges like CAPTCHA.
Model Scale Limitations: The publicly available 7B version is less optimized for specialized scenarios like gaming compared to the more restricted 72B version.
What’s next: future development roadmap
ByteDance has outlined an ambitious roadmap for UI-TARS, focusing on several key directions:
Active and lifelong learning
Future versions will evolve toward agents that autonomously drive their own learning through continuous real-world interactions, enabling:
- Self-improvement through analysis of successful and failed interactions
- Adaptation to new interfaces without explicit retraining
- Progressive skill development through experience accumulation
Enhanced agentic capabilities
ByteDance plans to develop increasingly sophisticated capabilities:
- Handling more complex real-world tasks involving multiple applications
- Better contextual understanding across extended sessions
- More nuanced error recovery and alternative path exploration
Integration with other ByteDance platforms
Plans include empowering platforms like Doubao to accomplish more complex tasks through UI-TARS technology, potentially extending the model’s reach to enterprises and consumers through existing ByteDance products.
Developer accessibility
ByteDance is focused on making the technology more accessible by offering:
- Expanded cross-platform SDK options for developers
- Simplified cloud deployment through platforms like ModelScope
- Better documentation and community support resources
The reality check: limitations, challenges, and ethical considerations
Despite its impressive capabilities, UI-TARS comes with important limitations and ethical considerations.
Technical limitations
Computational Requirements: The most capable models require substantial resources, limiting deployment options.
Hallucination Issues: The model may occasionally generate inaccurate descriptions or take suboptimal actions based on misinterpretations, especially in ambiguous environments.
Performance in Novel Environments: While adaptable, UI-TARS still performs best in interface types it has encountered during training.
Ethical considerations
Privacy and Security: The model’s screen-reading capabilities raise questions about data privacy when interacting with sensitive information.
Potential for Misuse: ByteDance acknowledges risks related to unauthorized access, particularly given the model’s ability to bypass CAPTCHAs and other security measures.
Job Displacement: Advanced automation capabilities could impact jobs focused on repetitive GUI-based tasks, though they may create new opportunities in agent development and supervision.
ByteDance has implemented several measures to address these concerns, including:
- Extensive internal safety evaluations
- Transparent documentation of limitations
- Open-source licensing to enable community oversight
- Structured model release approach, with more powerful models having limited availability
Industry experts suggest that while the technology offers significant benefits, it requires thoughtful governance and usage policies to ensure responsible deployment.
The latest breakthrough: UI-TARS-1.5 (April 2025)
Released in April 2025, UI-TARS-1.5 represents ByteDance’s most advanced GUI automation agent, with several key improvements over previous versions:
Enhanced Reasoning: Improved System-2 deliberate reasoning with more sophisticated planning capabilities, especially notable in gaming environments.
Performance Gains: Dramatic improvements across all benchmarks, achieving a 42.5% success rate on the challenging OSWorld 100-step benchmark.
Mobile Excellence: Significant advances in mobile automation capabilities, with a 64.2% success rate on Android World tasks.
Gaming Proficiency: 100% task completion rate across 14 Poki mini-games, demonstrating versatility in gaming environments.
Improved Grounding: Exceptional performance in ScreenSpotPro (61.6%), more than doubling the accuracy of competitors like OpenAI Operator (23.4%).
The release includes both UI-TARS Desktop v0.1.0 with a redesigned Agent UI and expanded SDK options for developers. The 7B version is publicly available on Hugging Face under the Apache 2.0 license, while the more powerful 72B version has more limited research access.
ByteDance’s iterative training approach, using reflective online traces and direct preference optimization, has resulted in a model that not only understands GUI elements but can reason through complex multi-step tasks with greater reliability.
Conclusion
ByteDance’s UI-TARS represents a significant leap forward in GUI automation, integrating perception, reasoning, and action capabilities in a unified architecture that operates across platforms with near-human proficiency. While challenges remain in computational requirements and potential misuse, the technology’s open-source nature and impressive performance benchmarks position it as the current leader in this rapidly evolving field.
As UI-TARS continues to develop, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated applications in productivity, accessibility, software testing, and enterprise automation. The balance between innovation and responsible deployment will be crucial as these capabilities become more widely available and integrated into our digital experiences.